|
Microwave Radiometry
Microwave Radiometry is based on measuring the intensity of natural electromagnetic radiation from a patient's tissue at microwave frequencies. This intensity is proportional to the temperature of tissue.
The change in temperature (thermal abnormality), that is a basis of earlier detection of breast cancer, may be caused by increased cancer cell metabolism.
It should be noted that thermal changes precede to the anatomical changes that can be detected by traditional methods such as ultrasound, mammography and palpation.
Thus microwave radiometry is a very promising method for the breast cancer detection at an earlier stage.
Basis of Microwave Radiometry
Microwave Radiometry is based on measuring the intensity of natural electromagnetic radiation from a patient's tissue at microwave frequencies.
This intensity is proportional to the temperature of tissue. So we can say that microwave radiometry allows one to measure the internal temperature and display it on the monitor.

Difference between Microwave Radiometry and Infrared Thermography
The main difference between well known infrared thermography and microwave radiometry is that the former allows to read and display the skin temperature, when the latter indicates the internal temperature.
Advantages of Microwave Radiometry
1. Non-hazardous
Microwave Radiometry is non-hazardous both to the patients and to the personnel taking the thermograms, as during the examination the intensity of natural electromagnetic radiation from the patient's tissue is measured.
2. Non-invasive
Temperature is measured non-invasively.
3. Earlier detection of diseases
Thermal changes precede to the anatomical changes that can be detected by traditional methods such as ultrasound, mammography and palpation. Thus microwave radiometry is a very promising
method for the breast cancer detection at an earlier stage.
4. Detection of fast growing tumors
The specific heat generation in the tumor is proportional to the grow rate of the tumor. So fast growing tumors are "hotter" and they are more contrast in thermograms.
Thus microwave radiometry is an unique method that allows to detect first of all fast growing tumors. Using microwave radiometry (RTM-Diagnosis) in conjunction with other tradition methods allows
o select patients with fast growing tumors.
5. Ability to detect patients with increased proliferative activity of cells
The important feature of the microwave radiometry is that it can distinguish proliferative mastopathy and fibroadenoma from non-proliferative mastopathy and fibroadenoma. So the method allows to select patients who risk to have breast cancer.
6. Ability to monitor treatment
Microwave Radiometry is non-hazardous both to the patients and to the personnel taking the thermograms, so it can be effectively used for the monitoring of the treatment.
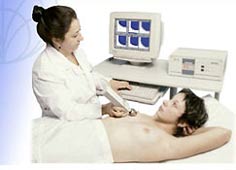
Medical Radiometer RTM-01-RES
Microwave thermography, or, more correctly, radiometry, with is defined as the measurement of natural electromagnetic radiation or emission from the body at microwave frequencies to allow
the detection and diagnosis of pathologic conditions in which there are disease related temperature differentials. The application of radiometry has, for the most part, been directed at the early
detection and diagnosis of breast cancer.
    
Present detection techniques other than radiometry require that the tumor have mass and contrast with respect to the surrounding tissue (i.e., palpation physical examination, mammography,
ultrasonography and diaphonography). Early detection could lead to a more conservative treatment and a positive attitude toward detection. Suspicious results found by screening using microwave
radiometry could then referred for mammography.
Radiometric techniques represent a passive, noninvasive, noninonizing procedure determining thermal activity rather than mass that, when used in conjunction with one or of the other methods,
could provide early detection. The determination of thermal activity is a measurement of tumor activity, or growth rate, providing date beyond the physical parameters (i.e., size and depth determined
by mammography)
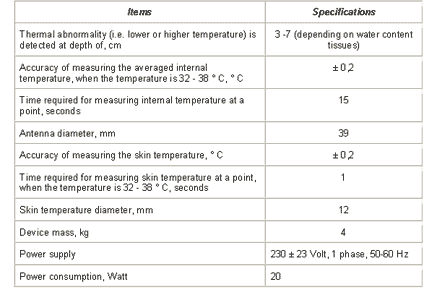
The device specifications are the following:
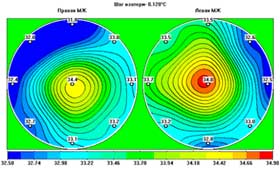
Ductal cancer is accompanied with a considerable increase in nipple
temperature (1-1.5° C) as well as a significant thermal asymmetry
at one point. (Fig 6.).
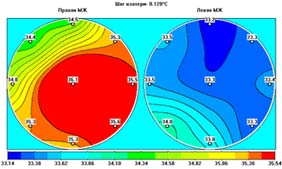
Inflammatory cancer is accompanied with a 1-1.50 ? increase in the
temperature of the most part of the damaged breast. (Fig. 7)
The same conditions accompany acute mastitis. However the fact that
the method is harmless, if there is any suspicion of this disease,
the patient may be treated with drugs and then the RTM-results obtained
before and after treatment may be compared. (Fig. 8)
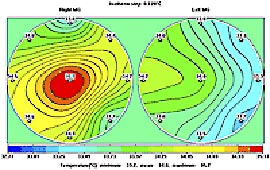
Fig.8 Before treatment
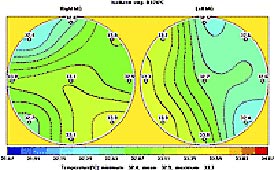
Fig.8 b) After treatment
The RTM-01-RES internal tissue temperature computer-based radiometer
is recommended for using in medicine practice for screening at consulting
and oncology rooms and at specialized oncology and mammology centers
for detection of breast cancer and the monitoring of treatment.
|